# What is a Preprocessor?
A preprocessor is a tool, that performs transformations on source code before it is compiled/interpreted. It prepares code for the next stage of processing (which is compilation).
It removes unnecessary things in source code.
Preprocessor tasks:
- file inclusion
- macro expansion
- conditional compilation
replaces inclusion/macros with corresponding code.
# How a preprocessor works
-
In C - preprocessor is part of compilation process - it handles macros & directives in source code. Macroprocessor - tool that performs textual transformation based on predefined rules (macros). Macros are defined using
#define -
preprocessor - automatically invoked by C compiler (part of compilation process)
-
preprocessor - operates on source code - before it is passed to compiler. Goal: prepared source code for compilation stages. Transformations it performs:
- inclusion of files (header files)
- macro expansion
- conditional compilation
- …
Sequence - compilation of HLL
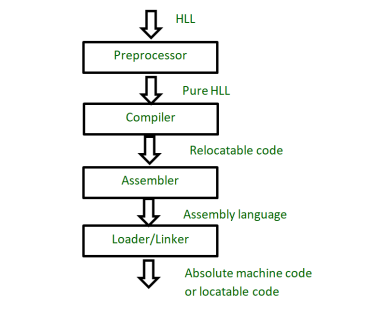
Stages explained:
- programmer writes code in HLL (e.g. C)
- preprocessor handles macros & directives (automatically invoked by C compiler)
- After preprocessing - still HLL form, but certain modifications done by preprocessor = in Pure HLL
- compiler generates LLL form - can be understood by computer’s architecture = Relocatable code (can run on different memory locations)
- assembler translates relocatable code into machine/binary code = Assembly language
- loader/linker combine object files - load executable program into memory
- ouput of linker = binary representation of program - ready to be executed by computer = Absolute Machine Code / Locatable Code (located memory address)