# Introduction
Trees are data structures commonly used in computer science and databases to efficiently store and manage large sets of data, particularly in scenarios where data needs to be inserted, deleted, or searched quickly.
# Tree Structures
Here are some sample Tree Structures & how to use them.
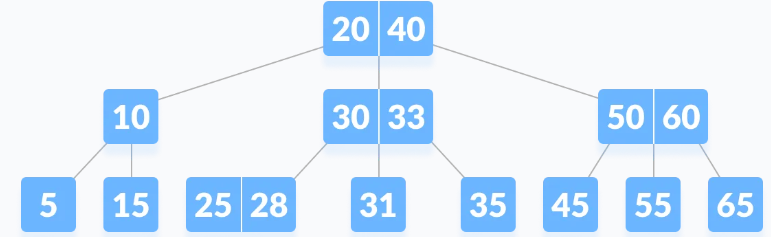
# B-Tree
Balanced-Tree
B-tree is a special type of self-balancing search tree in which each node can contain more than one key and can have more than two children. It is a generalized form of the binary search tree.
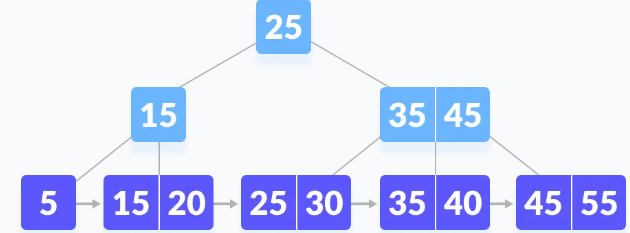
# B+Tree
Balanced-Plus-Tree
A B+ Tree is an advanced form of a self-balancing tree in which all the values are present in the leaf level.
- data gets only saved in leafs
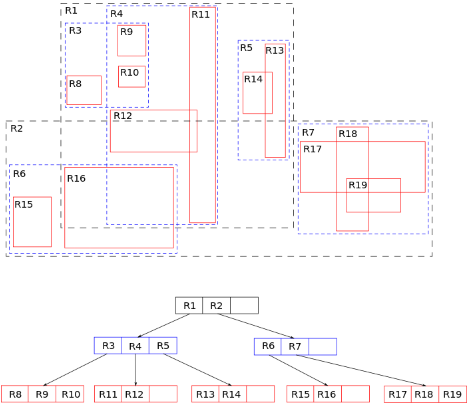
# R-Tree
Rectangle-Tree
R-Tree is used for spatial indexing, commonly employed in spatial databases and geographic information systems (GIS) - by rectangles.
# How the index works
An index in an R-Tree works like a smart map. It divides the space into boxes, each holding info about objects in that area - from one quadrant to the next. When you look for something in a specific zone, you check the tree and quickly find the relevant details.