# Note
Here wer gonna explain Bitmasks & how to use them in C
# Bitmasks: set of (independent) bits
set(1) / unset(0)
Bitmasks are a fundamental concept in computer science and low-level programming, particularly when working with individual bits within data.
- Data is saved as bit information
- can be thought of as tiny switches: on(1) / off(0)
- not seen as a number (int, char, …)
- efficient and compact storage
- data is processed as Boolean Logic
- can use bitwise operators (AND, OR, XOR, NOT) to manipulate bits in bitmask
- A bit saves True (1) / False (0)
# Logic Operations for Bit Masking
# Inverting (not)
- Inverts bitwise (1 → 0, 0 → 1)
- ”~” operator
// %X = hex formatter
// %08 print at least 8 numbers
int not 0x3; // 0011b
int res = ~not;
printf(" 0x%08X inverted => 0x%08X", not, res);
// Output: 0x00000003 inverted => 0xFFFFFFFC# AND
- Bitwise logical and
- ”&” operator
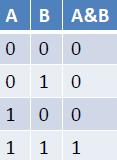
int A = 0x3; // 0011b
int B = 0x9; // 1001b
int res = A&B;
printf(" 0x%02X & 0x%02X => 0x%02X", A, B, res);
// Output: 0x03 & 0x09 => 0x01# OR
- Bitwise logical or
- ”|” operator
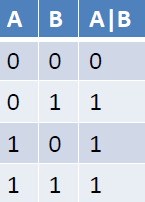
int A = 0x3; // 0011b
int B = 0x9; // 1001b
int res = A|B;
printf(" 0x%02X | 0x%02X => 0x%02X", A, B, res);
// Output: 0x03 | 0x09 => 0x0B# XOR
- Bitwise logical or
- ”^” operator
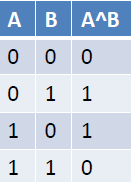
int A = 0x3; // 0011b
int B = 0x9; // 1001b
int res = A^B;
printf(" 0x%02X ^ 0x%02X => 0x%02X", A, B, res);
// Output: 0x03 ^ 0x09 => 0x0A# Shift Operations
# Right shift
- ”>>” operator
- ”A >> n” shift right for n digits
- LSBs are dropped
- Leading bits are filled with zeros
- Division by two
- Only positive shift count (compiler dependent)
int A = 0x3; // 0011b
int res = A >> 1;
printf(" 0x%02X >> 1 => 0x%02X", A, res);
// Output: 0x03 >> 1 => 0x01# Left shift
- ”<<” operator
- ”A << n” shift left for n digits
- MSBs are dropped
- LSBs are filled with zeros
- Multiplication by two
- Only positive shift count (compiler dependent)
int A = 0x3; // 0011
int res = A << 1;
printf(" 0x%02X << 1 => 0x%02X", A, res);
// Output: 0x03 << 1 => 0x06