# What are “Ports"
"ports” typically refer to groups of I/O pins - each port is associated with a specific pin. Ports allow you to interact with external devices, sensors, … .
# Keypoints of Ports in Microcontrollers
- General digital I/O Ports
- sets of pins on a microcontroller
- Read-modify-write functionality
- pin driver is strong enough - drive LED displays directly
- Port pins have individual selectable pull-up resistors
- you can configure pins - to do different tasks
# I/O Ports schematic
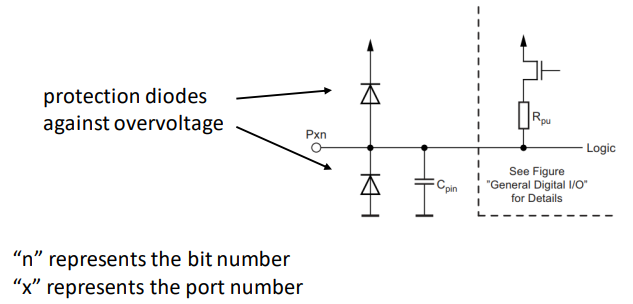
# I/O Ports
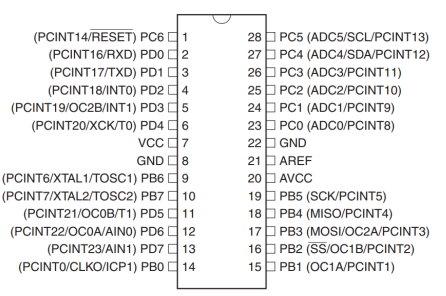
# Configuring the pins
# Sample Keywords
input : read data from sth
output : controll & drive external components
HIGH : powered on [1]
LOW : powered off [0]
- Port pin consists of 3 register bits
- DDxn: selects data direction of the pin
- 1 … output pin
- 0 … input pin
- PORTxn: configuring the pins
- input pin:
- 1 … internal pullup activated
- 0 … internal pullup deactivated
- output pin:
- 1 … pin is driven high
- 0 … pin is driven low
- input pin:
- PINxn: configuring the pins
- can be read through PINxn register bit
- DDxn: selects data direction of the pin
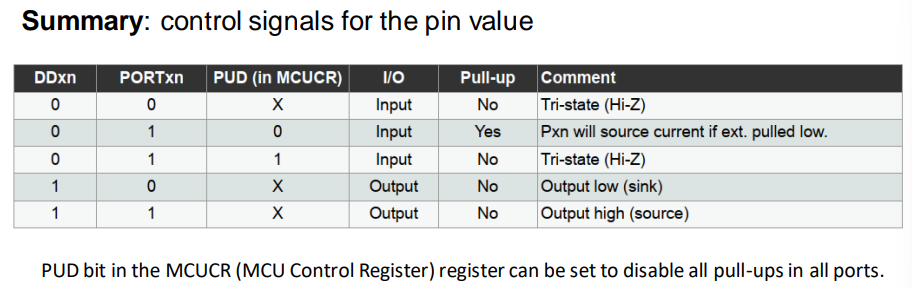
MCU Control Register - refers to a special type of memory location within the microcontrollers CPU.
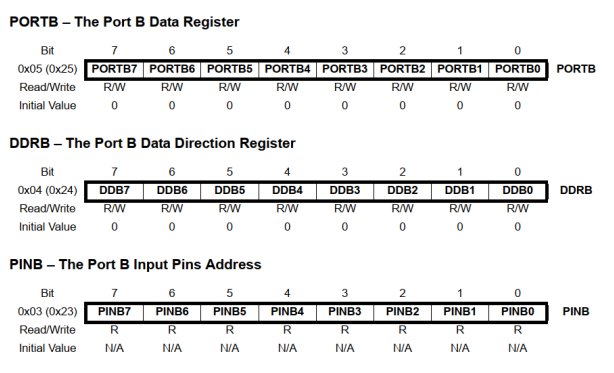
# Example: Register Configuration
for PortB in this example
# Configuration of Ports in C
Adresses and defines are in:
#include <avr/io.h>Example for PORTB:
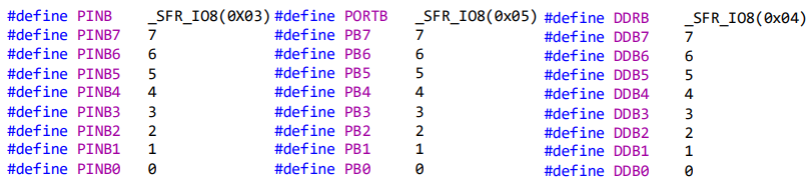
# Access to PORTB:
/* Set PORTB pin 2 to Output: */
DDRB |= 0b10;
/* Set PORTB pin 2 to HIGH */
PORTB |= 0x2;
/* Do some stuff */
/* Set PORTB pin 2 to LOW = 0b00000000*/
PORTB = PORTB & 0b11111101;