# What is Next.js ?
In simple words: Next.js is an extension of React.
It is fundamentally built on top of React. Its purpose is to simplify certain tasks. Allowing devs to concentrate on the core React code. It manages a bundle of features in itself:
- Routing
- Code splitting
- SEO
- automatic rendering
# Special Files
In Nextjs there are special files, that specify a specific usage.
- page.tsx / route.tsx - specify a route
- layout.tsx - UI shared across multiple pages
- +: on navigation, only page components update = layout won’t re-render (=‘partial rendering’)
# Next.js or React ?
# Rendering
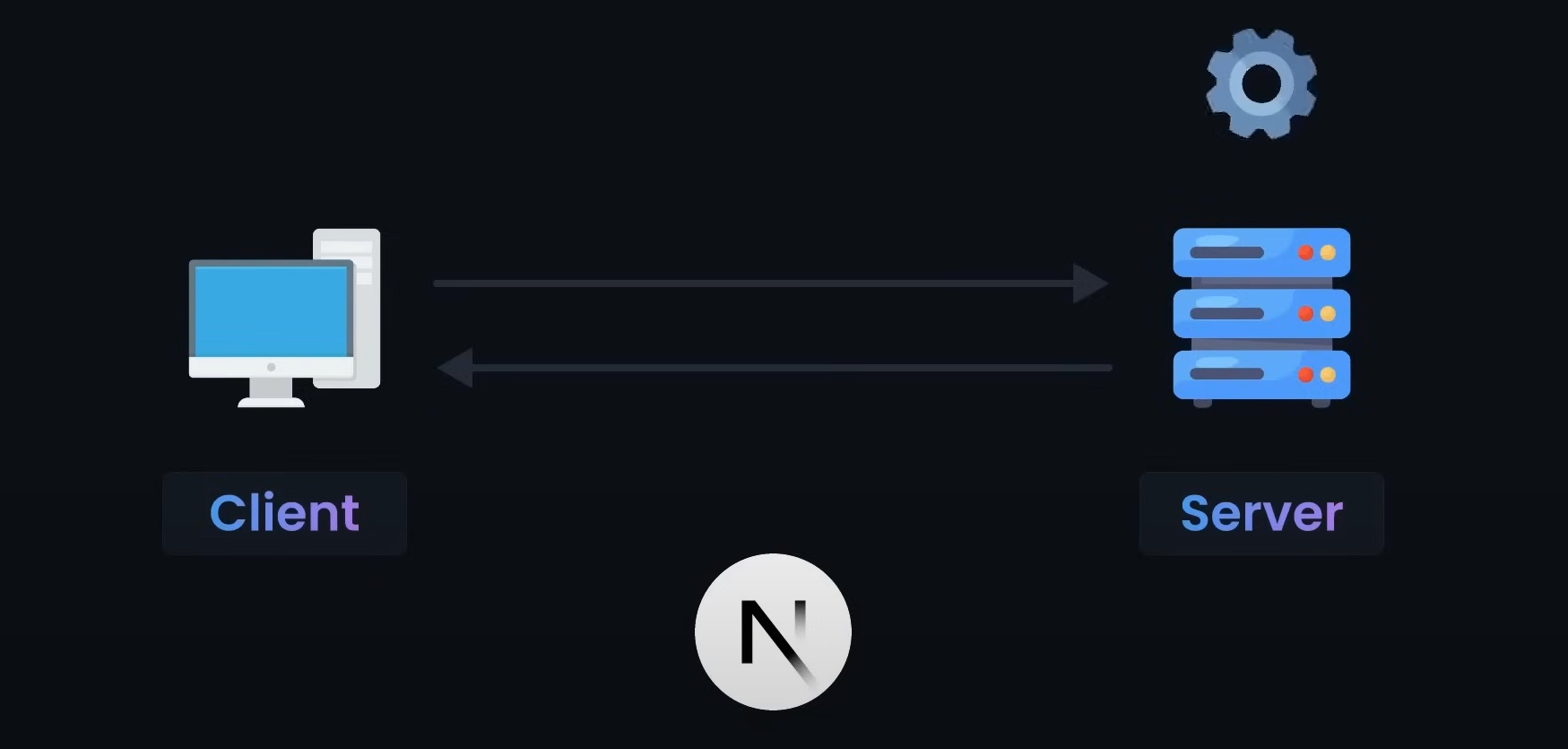
Their big difference lies on how they render things. Next.js supports SSR while React does not. Blazor_Introduction - for clear look on SSR & Client-Rendering
with React:

with Next.js:
# Routing
In React, you have to install an additional package React Router to manage page routes.
While Routes in Next.js are file-based. Meaning you don’t have to install external packages/complex configurations.
# Full-Stack ?
While React needs some configuration & installing packages when it comes to APIs, in Next.js API-Routes have been introduced in Next.js version 9.
# Code-Splitting
Code-Splitting is a technique that increases JS code a server has to send to the client.
When using React: you have to configure this. While in Next.js this completely happens behind the hood & you don’t have to worry about this.
# Rendering
It all begins with the rendering process. In Next.js, the website gets rendered on the server before it gets transmitted to the client’s device.
When a user requests a page - the server processes the request & sends back the complete site to the client
- called SEO “Search Enginge Optimization”
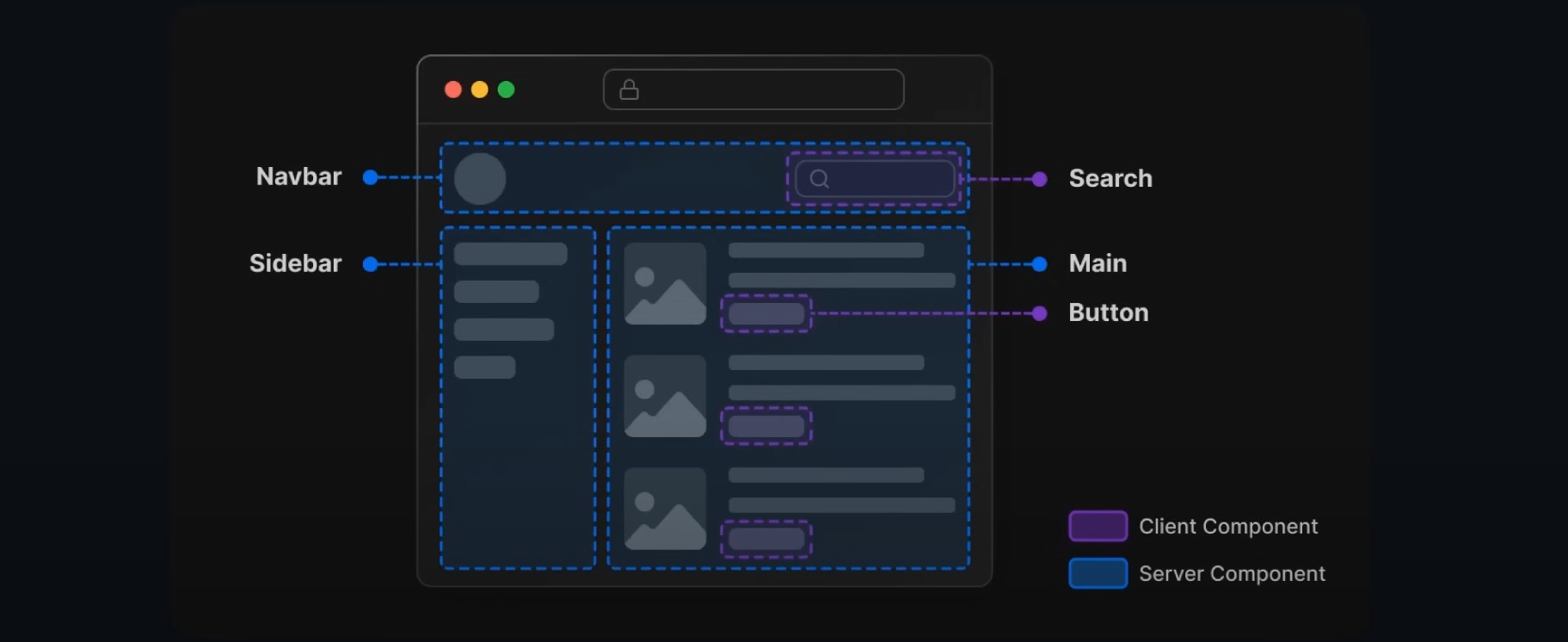
If you wanna use Client-Side-Rendering type "use client" on top of your component
# Routing
The routing in Next.js is file-based. The routing is handled by the file system. Meaning: Each folder gets an own route and the folder-name gets added to the route.
# API-Routes
Next.js can be used for frontend + backend apps. Traditionally using API-Routes. API-Routes enable a creation of serverless functions to handle API-requests. Serverless APIs in Next.js are a way of creating API endpoints - without the need for an additional server.
This allows us to build & deploy APIs
- without managing server infrastructure
- worrying about scalling the server - when requests increase
# File & Folder Structure
The app folder is the most important folder.
# app folder
# Layout.js
There is a RootLayout function, which displays all components/elements.
- typically, when you want to add something that should stay consistent (NavBar, Footer, …) place it in this file>RootLayout function.
# page.js
Represents the Home-Page route.
# globals.css
Contains the global css properties for the whole application.
# Routing - more Detail
# Nested Routing
In Next.js you only have to create a folder which has an folder inside. Looks like:
- Folder1
- Folder2
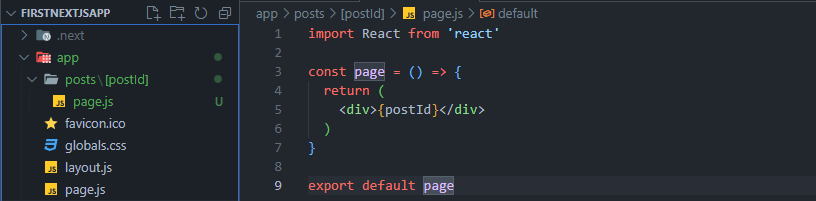
# Dynamic Routing
We want to have dynamic routes for all items. Folder/item1 Folder/item2 Folder/item3 …
Folder/:item
Dynamic Routes in Next.js
# Data Fetching
- SSR - Server Side Rendering
- SSG - Static Site Generation
- ISR - Incremental Static Generation
# Backend
using APIs
- GET
- POST
- PUT
- PATCH
- DELETE
- HEAD
- OPTIONS
Example for GET-Request in Next.js
// http://localhost:3000/api/users
export async function GET(request) {
const users = [
{ id: 1, name: "John" },
{ id: 2, name: "Jane" },
{ id: 3, name: "Bob" },
];
return new Response(JSON.stringify(users));
}