# Definition
series of guidelines for a DB
to organize & structure a DB to reduce redundancy and dependency issues, ensuring efficient storage, minimizing data anomalies
Several levels of normalization:
1. 0th Normal Form (0NF):
- Raw data, no structure
- Values in attributes are atomic
2. 1st Normal Form (1NF):
- Elimination of repeated groups
- Unique key identification
3. 2nd Normal Form (2NF):
- Elimination of partial key dependencies
- All non-key attributes fully functionally dependent on the entire key
4. 3rd Normal Form (3NF):
- Elimination of transitive dependencies
- No non-key attribute transitively dependent on a key
Dependencies between 0th, 1st, 2nd, and 3rd Normal Forms:
- 1NF eliminates redundancy of repeated value groups.
- 2NF eliminates partial key dependencies within the table.
- 3NF eliminates transitive dependencies between non-key attributes.
Transition from 0th to 1st to 2nd to 3rd Normal Form:
- 0NF to 1NF: Organize data into rows and columns, ensuring each attribute contains atomic values, eliminating repeating groups.
- 1NF to 2NF: Remove partial key dependencies by ensuring non-key attributes are fully functionally dependent on the entire primary key.
- 2NF to 3NF: Eliminate transitive dependencies, ensuring no non-key attribute depends on another non-key attribute through a key.
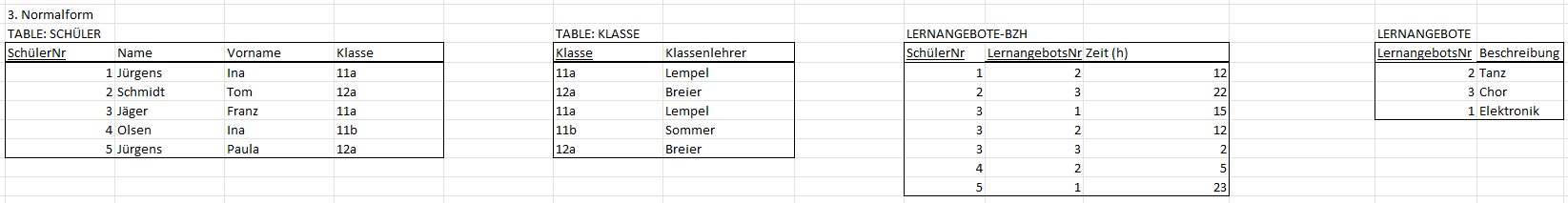
# Levels of Normalization
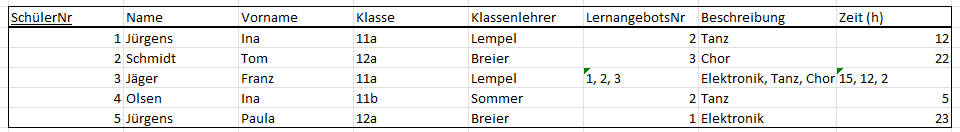
Example - Learning Opportunities
File
Transclude of Normalisierung_Lernangebotesübersicht.xlsx
Basic Table
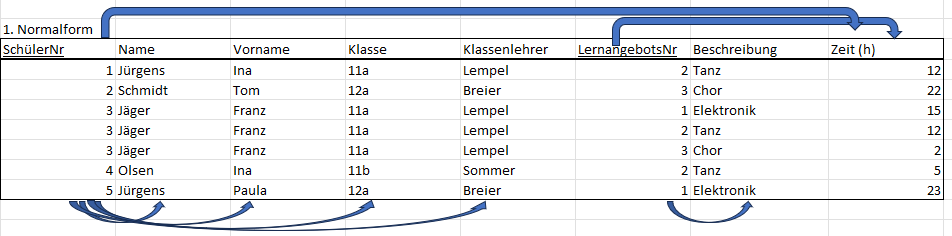
# 1st Normal Form
- all rows must be unique (no duplicate rows)
- every cell - only a single value (no list)
- each value - not divisible (not split down further)
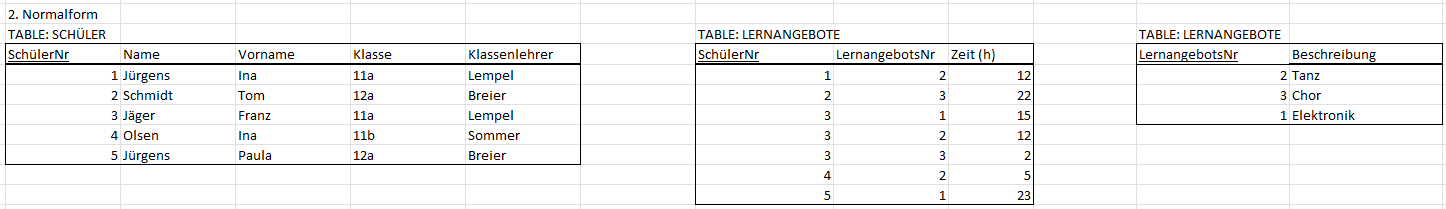
# 2nd Normal Form
- MUST BE IN 1st FORM
- all dependencies that don’t depend on primary key - should get an own table
# 3rd Normal Form
- MUST BE IN 1st & 2nd FORM
- no transitive dependency
- all fields must be determinable by the primary/compoite key - not by other keys
# Example - 1st Form
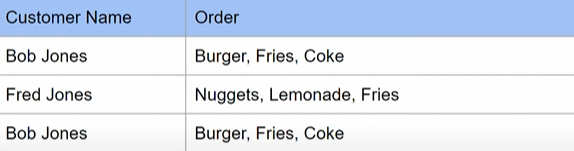
Problem 1 - All rows must be uniquely identifiable
- they are not uniquely identifiable
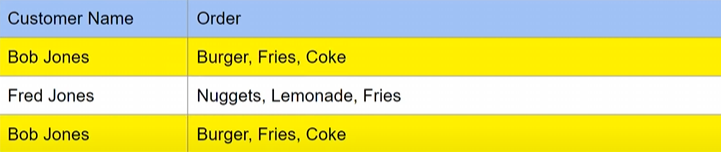
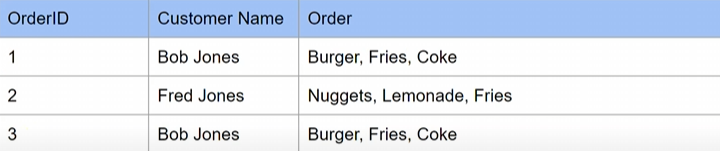
solution: Add an ID
- Now it is no longer identical - different IDs
Problem 2 - they have multiple values
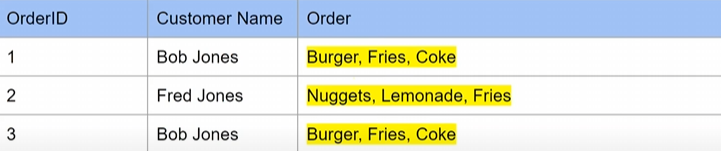
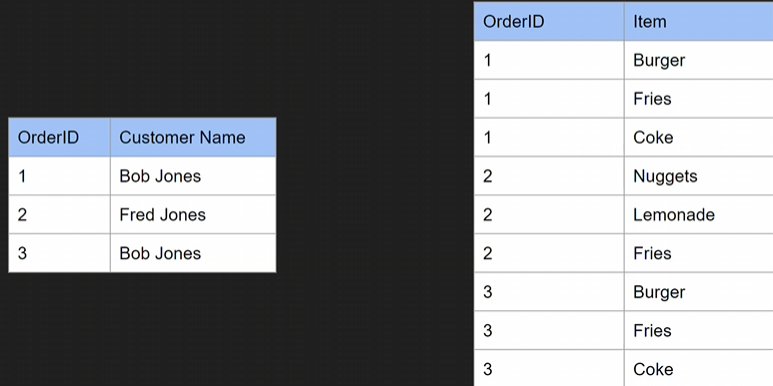
solution: seperate table
- Now we have a seperate table with order items
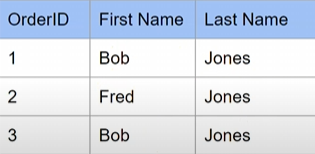
Problem 3 - all data must be atomic (non-divisible)
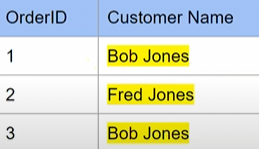
solution:
# Example - 2nd Form
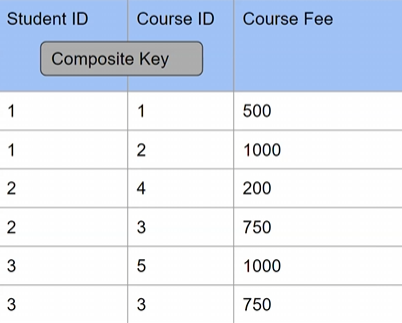
Problem 1 - no partial dependency
- Course Fee does not depend on Student ID
solution:
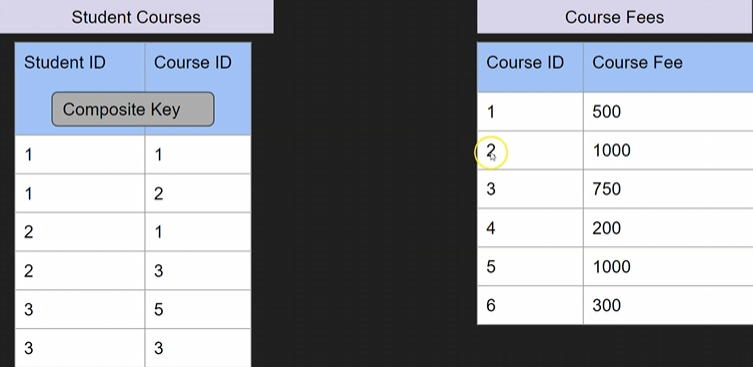
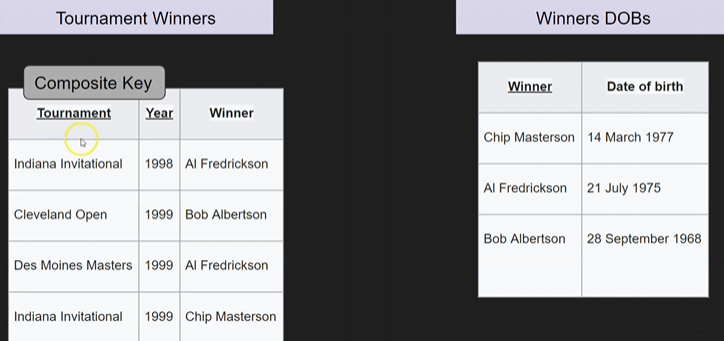
# Example - 3rd Form
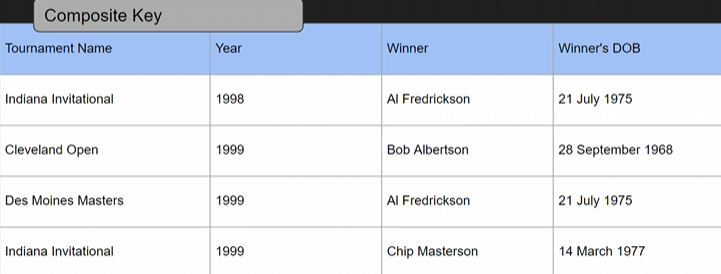
Problem 1 - no transitive dependency
- Winner’s DOB is dependend on the winner
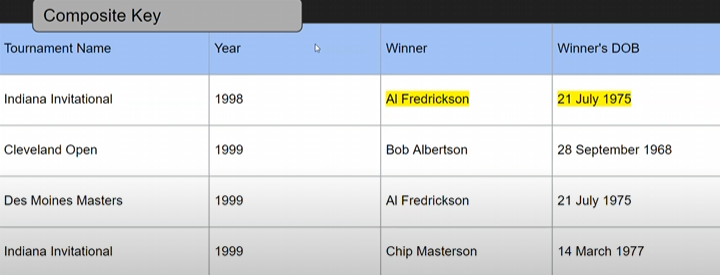
solution: