# Why Layers ?
Also see CSharp_EF-Core-Definition (Layers / Tiers)
Organizing code into layers is a common practice to promote maintainability, scalability & separation of concerns. The use of layers like API, Domain, Model helps in structuring the app.
# Breakdown
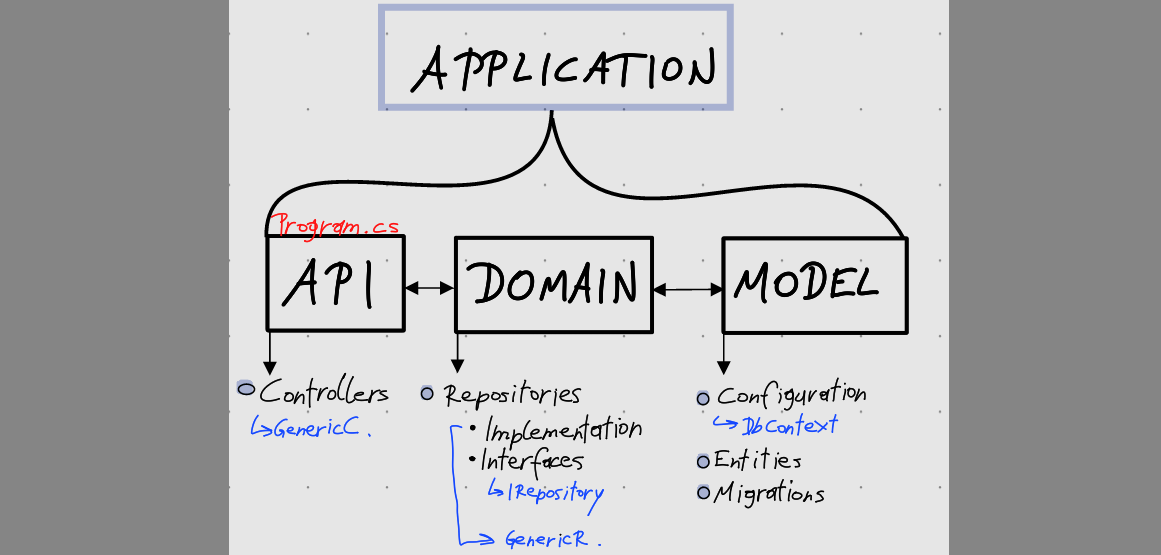
# Model
This layer manages configuration, entities, migrations.
- Configuration > DbContext
- Entities > Classes
- Migrations > Db-Migrations
# Domain
This layer is connected to the model using the DbContext. In this layer we can find Repositories
- Repositories
- Implementation > FirstRepository, SecondRespository, …
- Interfaces > IRepositoryBase
# Domain Interfaces
// IRepositoryBase.cs
public interface IRepositoryBase<TEntity, TId>
: where TEntity : class
{
Task<TEntity> CreateAsync(TEntity t);
Task<List<TEntity>> ReadAllAsync();
Task<List<TEntity>> ReadAsync(Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> filter, int start, int count);
Task<TEntity?> ReadIdAsync(TId id);
Task UpdateAsync(TEntity t);
Task DeleteAsync(TEntity t);
}# Domain Implementation
// RepositoryBase.cs
public class RepositoryBase<TEntity, TId>
: IRepositoryBase<TEntity, TId> : where TEntity : class
{
protected readonly YourDbContext Context;
protected readonly DbSet<TEntity> Table;
protected RepositoryBase(YourDbContext context)
{
Context = context;
Table = context.Set<TEntity>();
}
public async Task<TEntity> CreateAsync(TEntity t)
{
await Table.AddAsync(t);
await Context.SaveChangesAsync();
return t;
}
public async Task<List<TEntity>> ReadAllAsync() => await Table.ToListAsync();
public async Task<List<TEntity>> ReadAsync(Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> filter, int start int count)
{
return await Table
.Where(filter)
.Skip(start)
.Take(count)
.ToListAsync();
}
public async Task<TEntity?> ReadIdAsync(TId id)
{
return await Table.FindAsync(id);
}
public async Task UpdateAsync(TEntity t)
{
Table.Update(t);
await Context.SaveChangesAsync();
}
public async Task DeleteAsync(TEntity t)
{
Table.Remove(t);
await Context.SaveChangesAsync();
}
}Implementierung: TeacherRepository
- neue Methode (Konstrukturaufruf)
// TeacherRepository.cs
public class TeacherRepository(YourDbContext context)
: RepositoryBase<Teacher, int>(context);- alte Methode (Konstrukturaufruf)
// TeacherRepository.cs
public class TeacherRepository
: RepositoryBase<Teacher, int>
{
public TeacherRepository(TimetableDbContext context)
: base(context) { }
}# API
This layer is responsible for assigning data. For assigning data we use Api-Controller
- Controllers > GenericController, FirstController, …
# API Controller
Registration
// Program.cs
...
builder.Services.AddDbContextFactory<YourDbContext>(
options => options.UseNpgsql(
builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("Default"))
);
builder.Services.AddScoped<IRepository<Teacher, int>, TeacherRepository>();
builder.Services.AddControllers();
...
app.MapControllers();
...// GenericController.cs
public abstract class GenericController<TEntity, TId>(IRepositoryBase<TEntity, TId> repository)
: ControllerBase where TEntity : class
{
protected IRepository<TEntity, TId> Repository =
repository ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(repository));
[HttpPost]
public async Task<ActionResult<TEntity>> Post(TEntity item)
{
await Repository.CreateAsync(item);
return CreatedAtAction(nameof(Get), item);
}
[HttpGet]
public async Task<ActionResult<List<TEntity>>> Get()
{
return await Repository.ReadAllAsync();
}
[HttpGet("{id}")]
public async Task<ActionResult<TEntity?> GetById(TId id)
{
var result = await Repository.ReadIdAsync(id);
return result != null ? Ok(result) : null;
}
[HttpPut("{id}")]
public async Task<ActionResult> Put(TEntity item, TId id)
{
var result = await Repository.ReadIdAsync(id);
if(result is null)
{
return NotFound();
}
await Repository.UpdateAsync(item);
return NoContent();
}
[HttpDelete("{id}")]
public async Task<ActionResult> Delete(TId id)
{
var result = Repository.ReadIdAsync(id);
if(result is null)
{
return NotFound();
}
await Repository.DeleteAsync(result);
return Ok();
}
}// TeacherController.cs
[Route("[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class TeacherController(IRepository<Teacher, int> repository)
: GenericController<Teacher, int>(repository)