# What are Interrupts?
Signal, that immediatelly stops processor’s current task - handles urgent event.
- often triggered by external (peripheral) sources
Interrupts occur independently & asynchrony to running tasks (don’t wait for processor, till current task is finished).
An external device makes an IRG (interrupt request), signaling the processor to interrupt its current task & address a pending event.
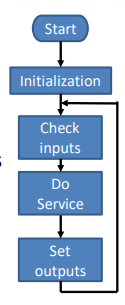
# Sequential Programming
”Polling” = permanently checks if something happens
- checks status of inputs, registers, sensors
- starting PC - starting a programm
- set things up - initialize variables, prepare environment
while (1) { - check inputs (polling) - checks if some input is made (e.g. pressing a Button)
- do service - condition is met - performs service
- set outputs - update state of things
}
# traps, exceptions, faults
something unexpected/wrong happened while execution of a program.
There are External Traps
- come from outside the program - problem with PCs memory, unable to access something (PCs memory - Bus error), …
And there are Internal Traps
- inside the program/PC itself - divide number by zero, breakpoints, …
# ISR
ISR = Interrupt Service Routine
each interrupt has own ISR.
when an interrupt occurs, ISR is executed.
most microcontrollers have fixed memory location with address of ISR = Interrupt Vector Table (IVT).
IVRlist that tells where to findISR