# Modelling Techniques
# Inheritance
# Weak/Strong Entity
# How to model data
# Modelling Techniques
ERD = Entity Relationship Diagrame
# Conceptual ERD
- Definition: Describes the high-level relationships between entities.
- Content: Entities and their relationships without specifying attributes.
- Purpose: Provides a conceptual overview of the data model.
- Use Case: Used during the initial planning stages to understand the relationships between different entities in the system.
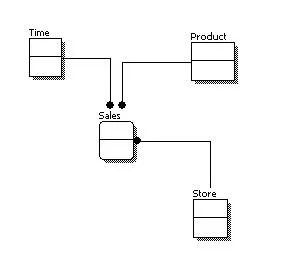
# Logical ERD
- Definition: Represents the structure of the database at a detailed level.
- Content: Includes tables, relationships, and attributes for each entity.
- Purpose: Serves as a blueprint for database implementation.
- Use Case: Used for designing and developing the database, defining the entities, their attributes, and the relationships between them.
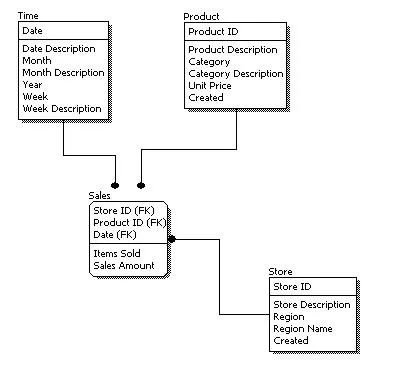
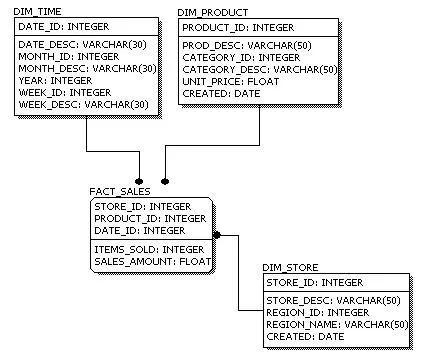
# Physical ERD
- Definition: Focuses on the implementation details and optimization.
- Content: Decides which columns need indexing for performance.
- Purpose: Guides database administrators in optimizing storage and query performance.
- Use Case: Used during the physical implementation of the database, considering factors like indexing and storage optimization for efficient performance.
# Inheritance
# One Table per Class
- Advantages:
- 1:1 mapping of the object-oriented model.
- Easily extendable for additional subclasses.
- Polymorphic queries (e.g., names/prices of all items) are straightforward.
- Disadvantages:
- Reads/Writes involve multiple tables, requiring joins.
- Non-polymorphic queries (e.g., names/prices of only drinks) can be cumbersome.
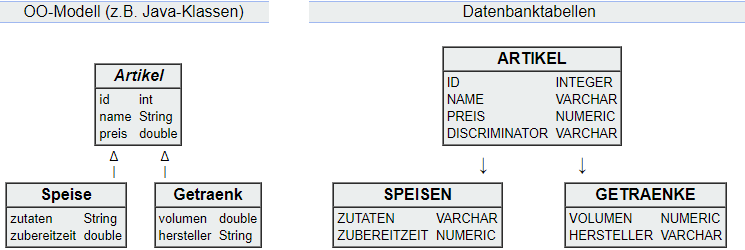
# One Table per Concrete Class
- Advantages:
- Easily extendable for additional subclasses.
- Reads/Writes involve only single tables, offering simplicity and good performance.
- Non-polymorphic queries (e.g., names/prices of only drinks) are simple.
- Disadvantages:
- Polymorphic queries are more complex as they require querying multiple tables.
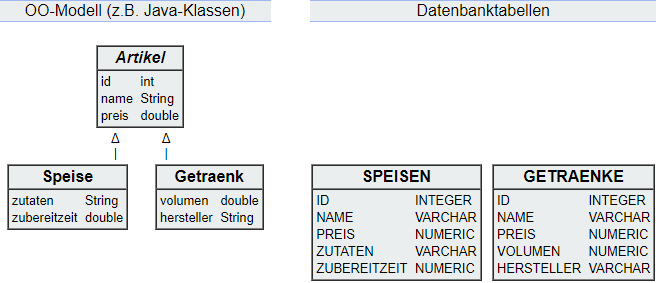
# One Table per Class Hierarchy
- Advantages:
- Reads/Writes involve only a single table.
- Polymorphic queries are straightforward.
- Disadvantages:
- Single table can become complex and hard to maintain.
- Lack of normalization may lead to storage inefficiency.
- Non-polymorphic queries can be cumbersome.
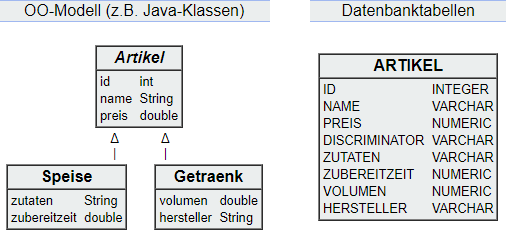
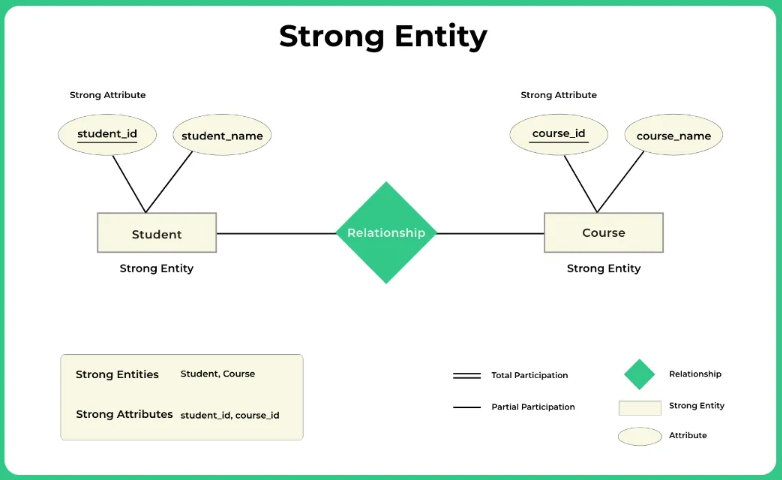
# Weak/Strong Entity
# Weak Entity
Only exists in association with a constraint
Example: A wage only exists - if the associated employee exists
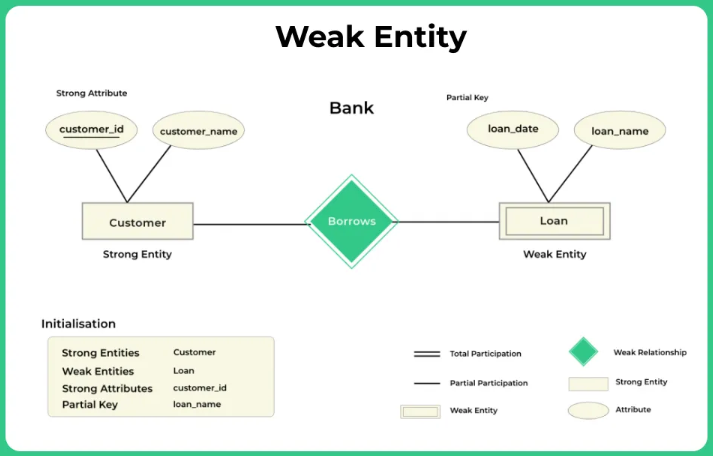
# Strong Entity
Table also exists without any other constraint - has own Primary-Key
Example: A course exists, even if no student visits it