Your goal in this exercise is to create a simple web application that stores its data within a database. Both the web application and the database should run in 2 separate containers and communicate with each other.
Tip
You will have to restart your containers several times during this exercise. To make sure, the image for your TodosApp will be rebuild every time, use the command docker-compose up -d --build (-d for detached and --build to force a rebuild of images when something changes).
Instructions
- Create your own Web Application using AspNetCore (Blazor is recommended) and name it TodosApp.
- Create a
docker-compose.yamlfile and describe your TodosApp. - Use
docker-composeto run your application in a container. - Check if the container is running (use the CLI and Docker Desktop).
- Note how docker compose names your containers!
- Check if your application is accessible through the specified port in your
docker-compose.yaml - Use
docker-composeto stop and remove your running containers and check if it was successful. - Your app should be capable of storing and retrieving Todos inside a database. The web view could look like this:
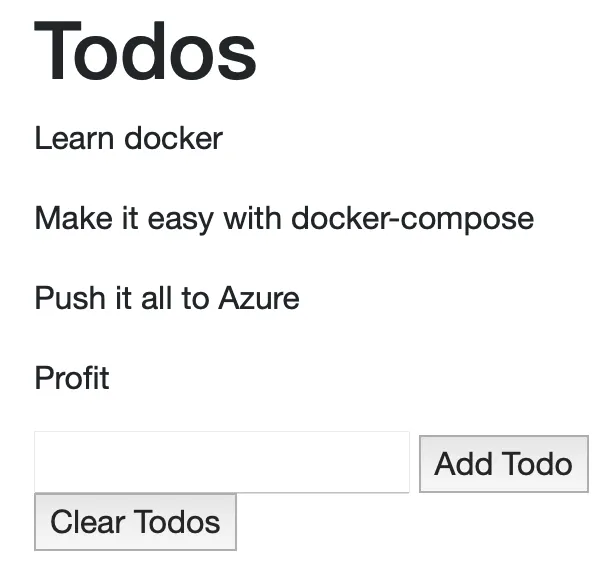
- You should be able to add single todo items by specifying a Title.
- You should be able to remove Todo Items (either single items, or all at once).
- You can choose different approaches for adding the database.
- Implement your database connection completely on your host system. This requires an accessible database. (either on your host system, or in a docker container with an exposed port)
- Define 2 services in your
docker-compose.yamlfrom the start and make sure the containers can communicate with each other
- Use an existing image from docker hub for your database. E.g.
mysql:8.2.0 - Make sure that your data is persisted through restarts of your application (using
docker-compose downanddocker-compose up). - Set any necessary (or useful) environment variables for your database (check the documentation on docker hub).
- Eventually make sure that both services (TodosApp and your database) are containerized and can be started through
docker-compose
Hints
You will probably stumble upon one problem if you try to containerize your app regarding database initialization. Up until now you probably followed the following steps for adding a database:
- Define your model
- Create a DbContext
- Add a migration
- Update the schema of your database
- Run the application
If you follow these steps, you will have to make sure, that running dotnet ef database update on your host system has access to your (already running) database container.
Another approach that you could look into is automatically running any pending database migrations from your TodosApp when the app starts. You can use the following code snippet in your Program.cs file to achieve this:
var scope = app.Services.CreateScope();
using var dbContext = scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<TodoDbContext>();
var connected = false;
while (!connected)
{
if (!dbContext.Database.CanConnect())
{
await Task.Delay(1_000);
continue;
}
dbContext.Database.Migrate();
connected = true;
}